Laser Cutting Head Composition
The laser cutting head is an important component of a laser cutting machine, mainly composed of the fiber connector block, collimation part, focusing part, protective lens housing, body, non-contact capacitive sensor, nozzle, and control system.
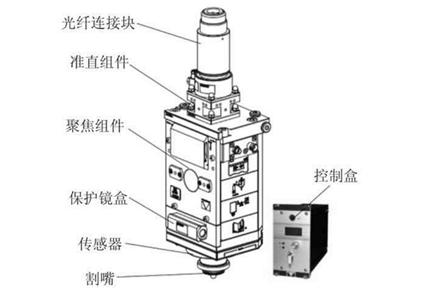
Cutting Head Composition
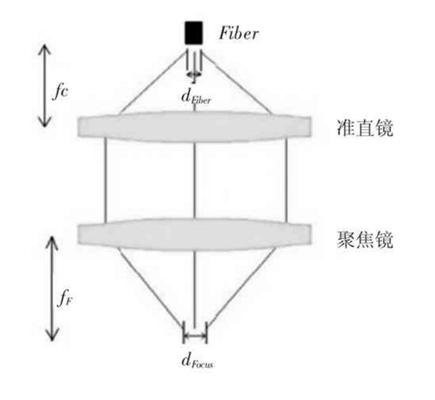
Cutting Optical Path
- Fiber Connector Block: The interface part where the fiber optic cable is connected to the cutting head. Common types include QBH, QD, QCS, and RK connectors, compatible with various lasers.
- Collimation Assembly: Converges divergent light into parallel light, including alignment and water cooling parts.
- Focusing Assembly: Located inside the body, it focuses the collimated light onto the workpiece and can adjust the focal point to accommodate different materials and thicknesses.
- Protective Lens Housing: Isolates external contaminants, protects the optical path from pollution, and extends lifespan.
- Sensor and Control Box: Stabilizes and controls the distance between the cutting head and the workpiece to ensure processing quality.
- Nozzle: Guides the laser and assist gas, removes molten material, and protects the lens while collecting signals.
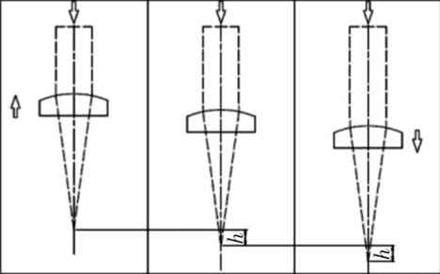
Selection and Adjustment of Focal Point and Sheet Position
Focal Point: The convergence point of parallel light after refraction by a lens or reflection by a curved mirror.
Application: The focal point position needs to be adjusted according to different materials and sheet thickness to ensure cutting quality.
- Thin carbon steel under 5mm: Zero focal length (focal point on the workpiece surface)
- Aluminum and stainless steel: Negative focal length (focal point below the workpiece)
- Thick steel plate: Positive focal length (focal point above the workpiece)
Note: Because the cutting head height and focal length are fixed, other methods must be used to adjust the focal point.
Methods: Two common focusing methods are:
- F-axis focusing: Adjusts the focal point by changing the vertical position of the focusing lens. When the lens moves down, the focal point moves down; it can be equipped with a motor for automatic focusing.
- VRM Focusing:A variable curvature mirror is added in front of the focusing lens. By adjusting the water pressure, the curvature of the mirror changes, thereby changing the beam divergence angle and focal point position.
- Water pressure increase: beam diverges → focal point moves downward.
- Water pressure decrease: beam converges → focal point moves upward.
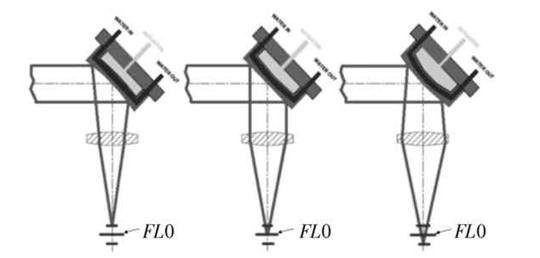
VRM Focusing
Principle: Through photoelectric and pressure...