Currently, for industrial applications involving metal materials, laser welding mostly uses fiber lasers and YAG lasers with wavelengths around 1064nm. This is mainly because metals have excellent absorption rates at this wavelength, resulting in superior processing quality. Below is a brief comparison of the two:
YAG Laser: A solid-state laser that generates laser light via optical excitation. It commonly uses a pulsed xenon lamp as the light source, with components including an optical pump, gain medium, resonator, focusing cavity, water cooling system, and power supply. Its advantage lies in lower equipment costs, but disadvantages include high power consumption and the need to replace lamps and other consumables. It is gradually being replaced by fiber lasers.
Fiber Laser: Consists of a resonator and a fiber gain medium. Its advantages include:
With the wave of Industry 4.0 and intelligent machinery, laser processing demonstrates great advantages in smart automation. In the 2018 Shanghai Optical Expo and Industrial Fair, many manufacturers exhibited laser welding systems.
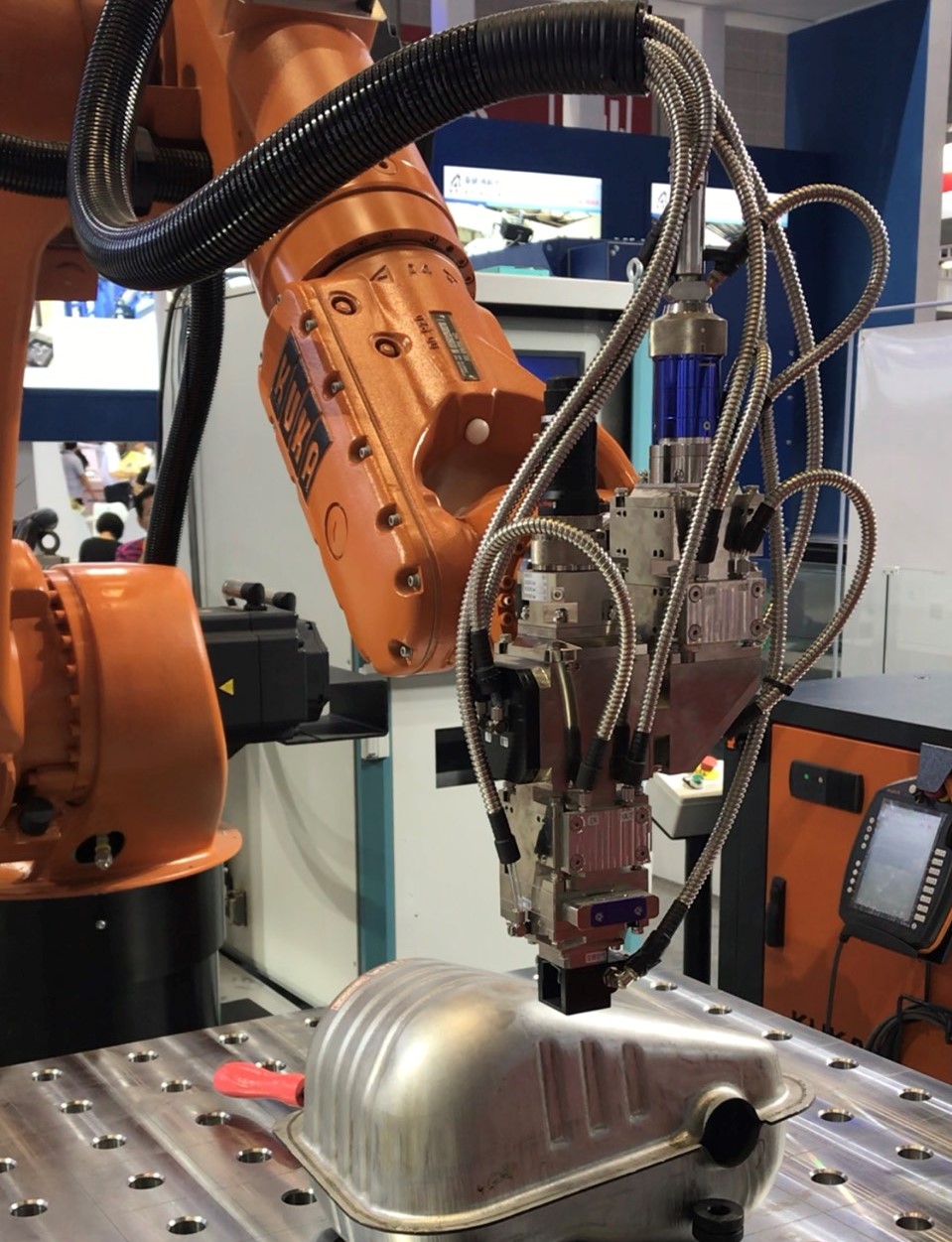
Figure 1: KUKA Laser Welding Robot at 2018 Shanghai Industrial Expo
1. Laser Welding Robots:
The most common are six-axis robotic arms capable of multi-directional welding. Combined with galvanometers and vision positioning, they can also achieve high-efficiency production through multi-station setups. Besides welding, they can also be used for cutting, cleaning, marking, and more.
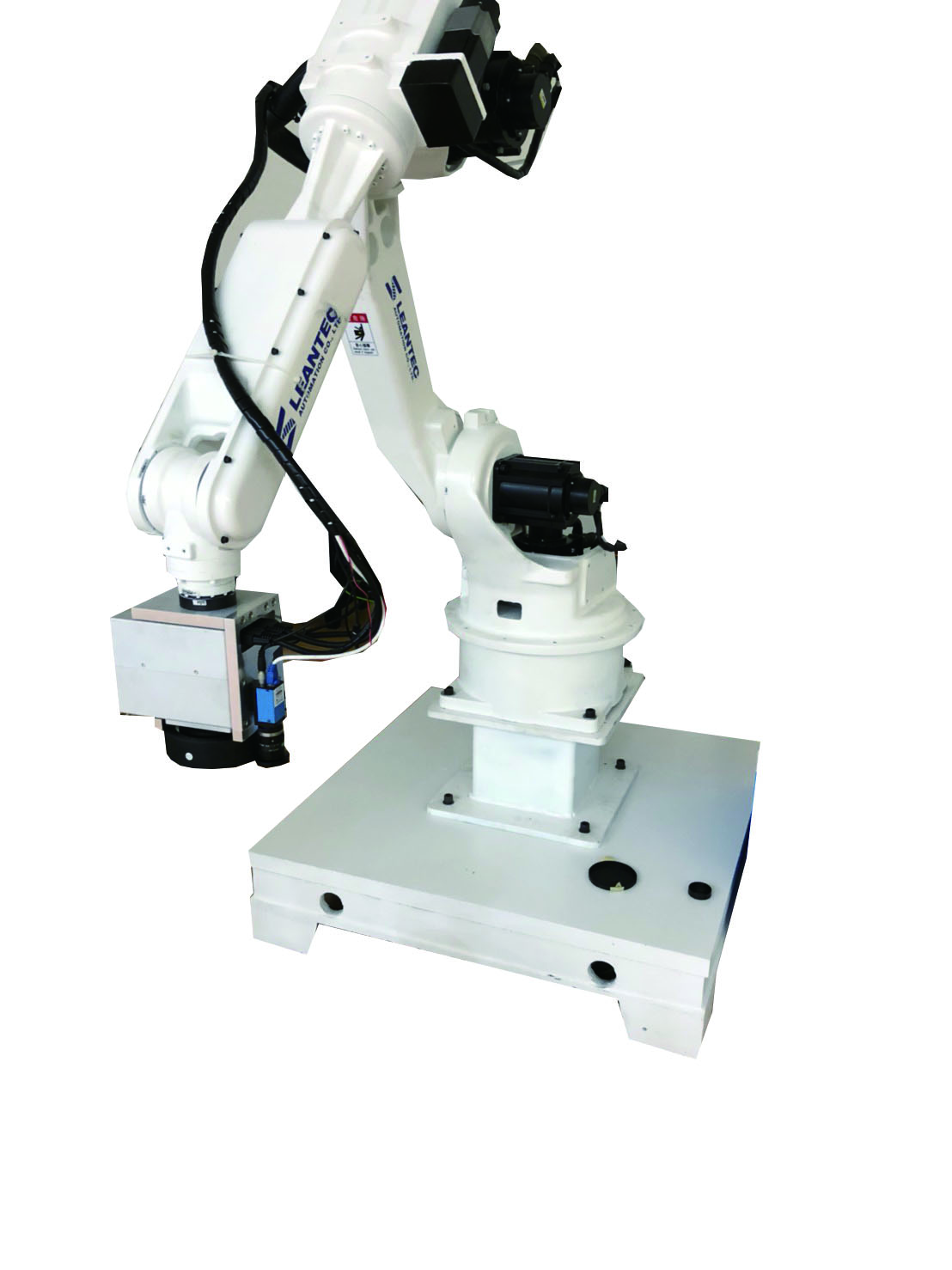 Figure 2: Lian Da Intelligent Company's Laser Galvanometer Vision Positioning Welding Robot
Figure 2: Lian Da Intelligent Company's Laser Galvanometer Vision Positioning Welding Robot
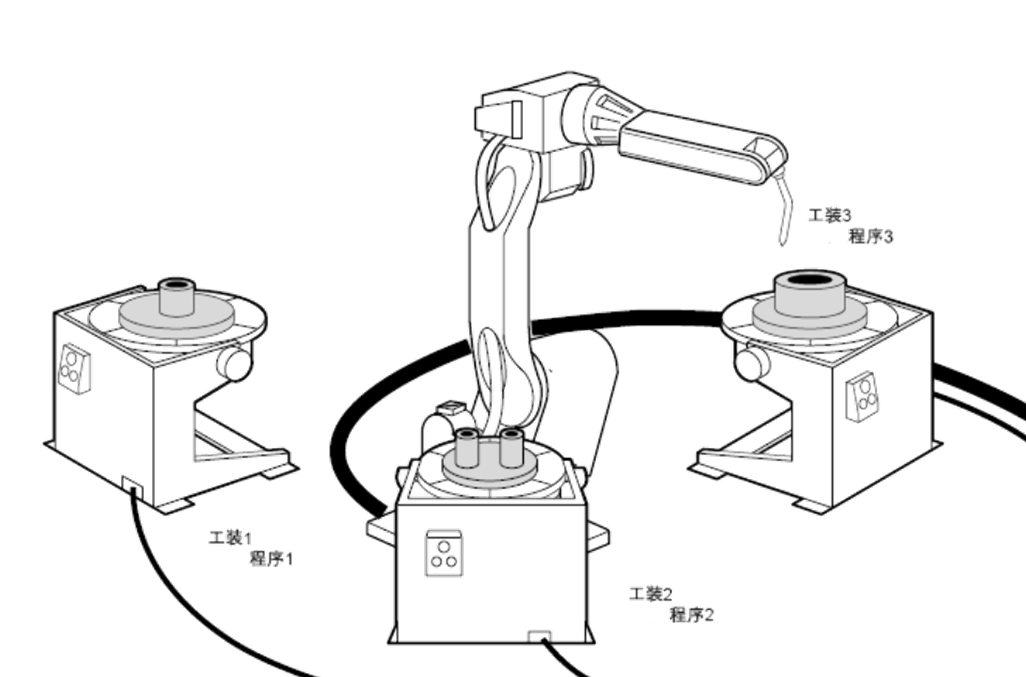
Figure 3: Multi-station Scheduled Welding System
2. Four-axis Linked Fiber Laser Welding Machine:
Includes X/Y/Z three-axis platform plus a W-axis rotary axis, coupled with CCD real-time focusing for high-precision welding. It can perform spot welding, butt welding, overlay welding, seam welding, sealing welding, and other processes.
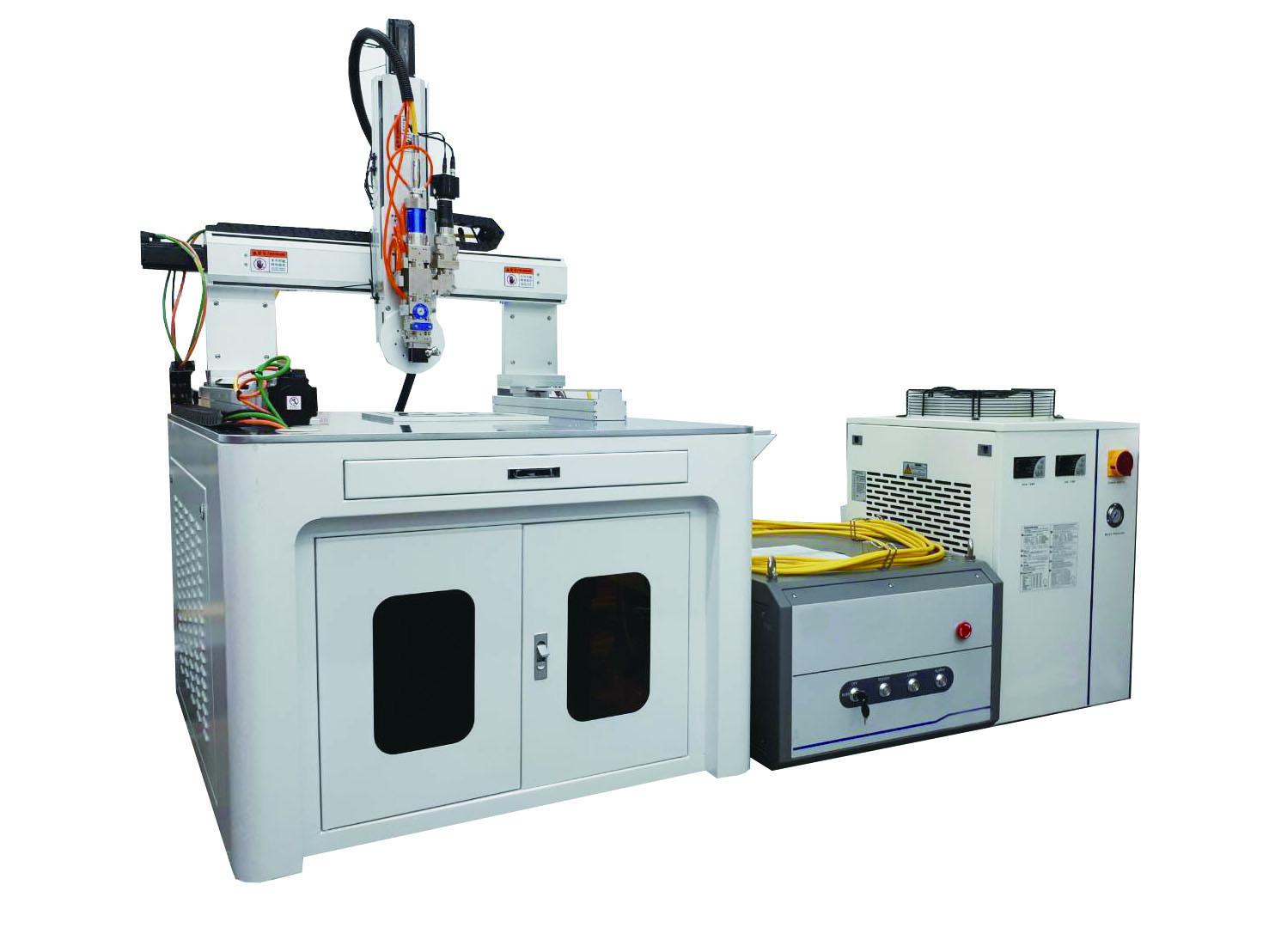

Figure 4: Four-axis Linked 2KW Fiber Laser Welding Machine Developed by Zhengbo Company
3. Weld Seam Tracking:
Through visual sensing, image processing, or laser scanning, automatic tracking of the weld seam prevents deviation, improves welding accuracy and quality, and reduces manual adjustment.
4. Stirring Welding Technology:
Using Wobble welding or galvanometer technology, the laser spot moves in a circular pattern, stirring the molten material to reduce pores and cracks, improving welding quality. It is especially suitable for wider weld seams.
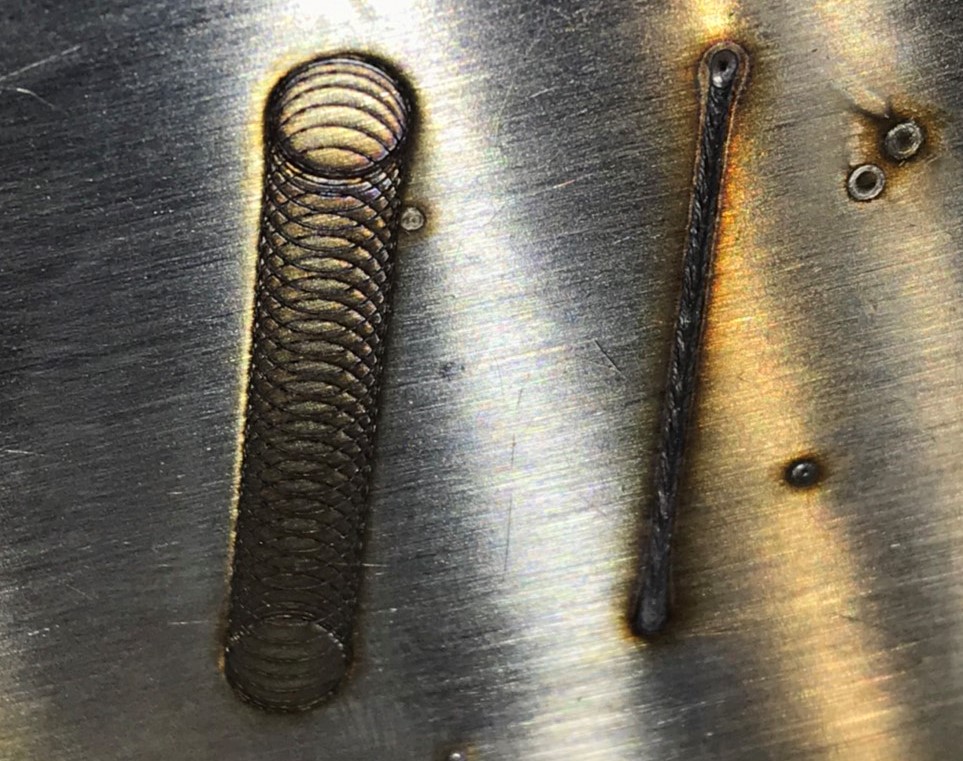

Figure 5: Illustration of Differences in Stirring Welding Laser Spots